April 3, 2025
AI reasoning vs non-reasoning models: key differences explained
By Sofía Sánchez González
When we talk about artificial intelligence, we can’t group all models into one. Perhaps the most significant difference lies in reasoning, since we can find models that—like some humans—are capable of reasoning. AI reasoning vs non-reasoning models: key differences explained.
Let’s start from the beginning
Before we dive into their differences, let’s begin at the root: What separates reasoning models from non-reasoning ones?
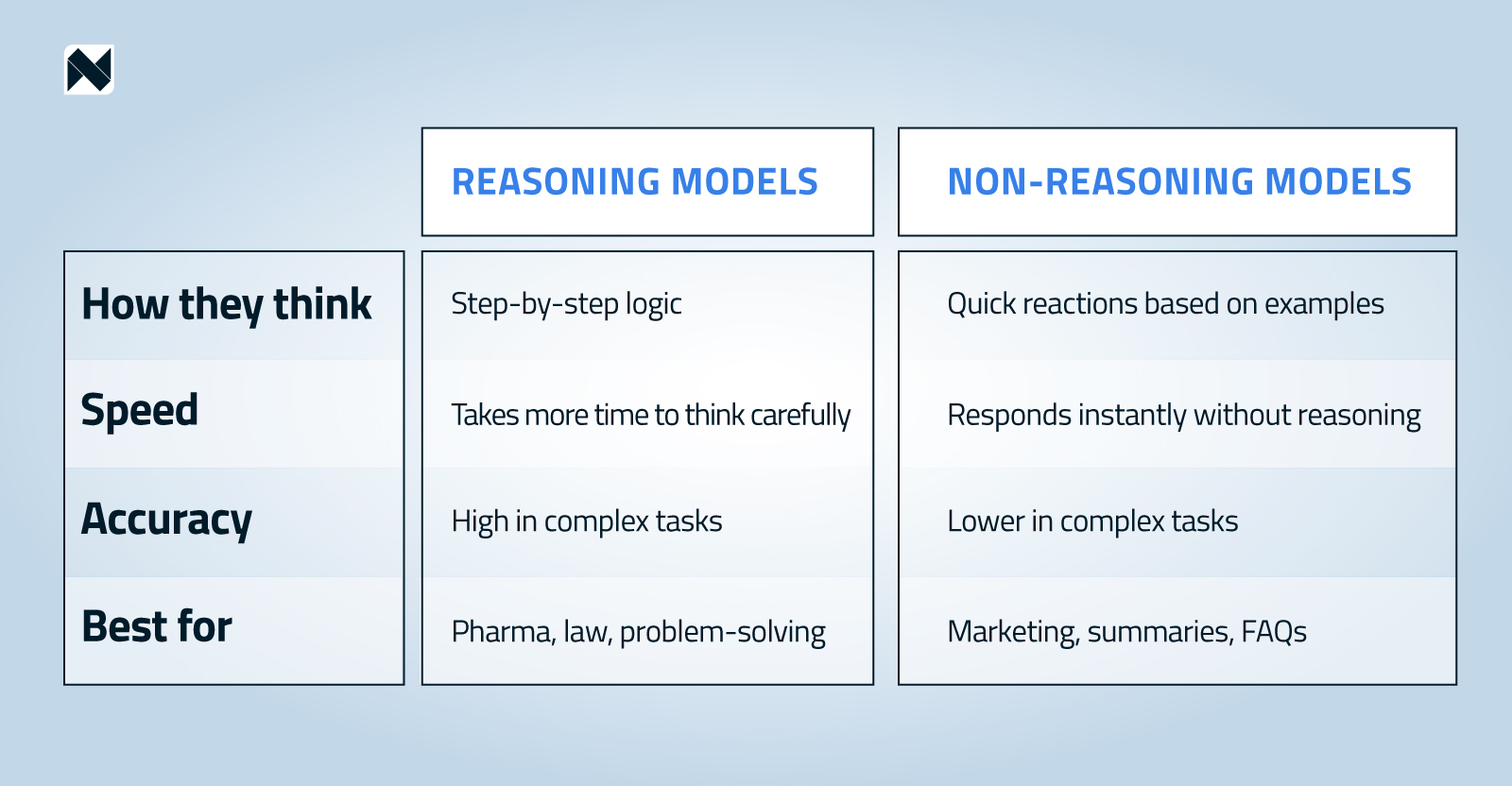
AI Reasoning models
Reasoning models follow logical steps to reach a response. They’re great for complex tasks because they seem to understand what they’re doing: they can solve difficult problems, draw their own conclusions, and even plan.
That means they take their time—like when we solve a math problem. Because these models need this extra time for reasoning and simulation, they tend to be a bit slower. However, they’re often more accurate as well.
AI reasoning models are trained using reinforcement learning, which helps them think in a more structured way. They receive verifiable rewards—rewards that can be checked, like when they reach the correct answer. In short: they’re told what’s right or wrong, but not how to get there.
Non-reasoning AI models
Non-reasoning models generate answers quickly by relying on learned patterns. These models don’t follow a step-by-step logical process—they just react. That makes them very fast, but also less reliable for tasks that require deep thinking or complex reasoning.
They’ve been trained on a kind of “book” full of examples, and they stick to that book. They don’t look for answers beyond it.
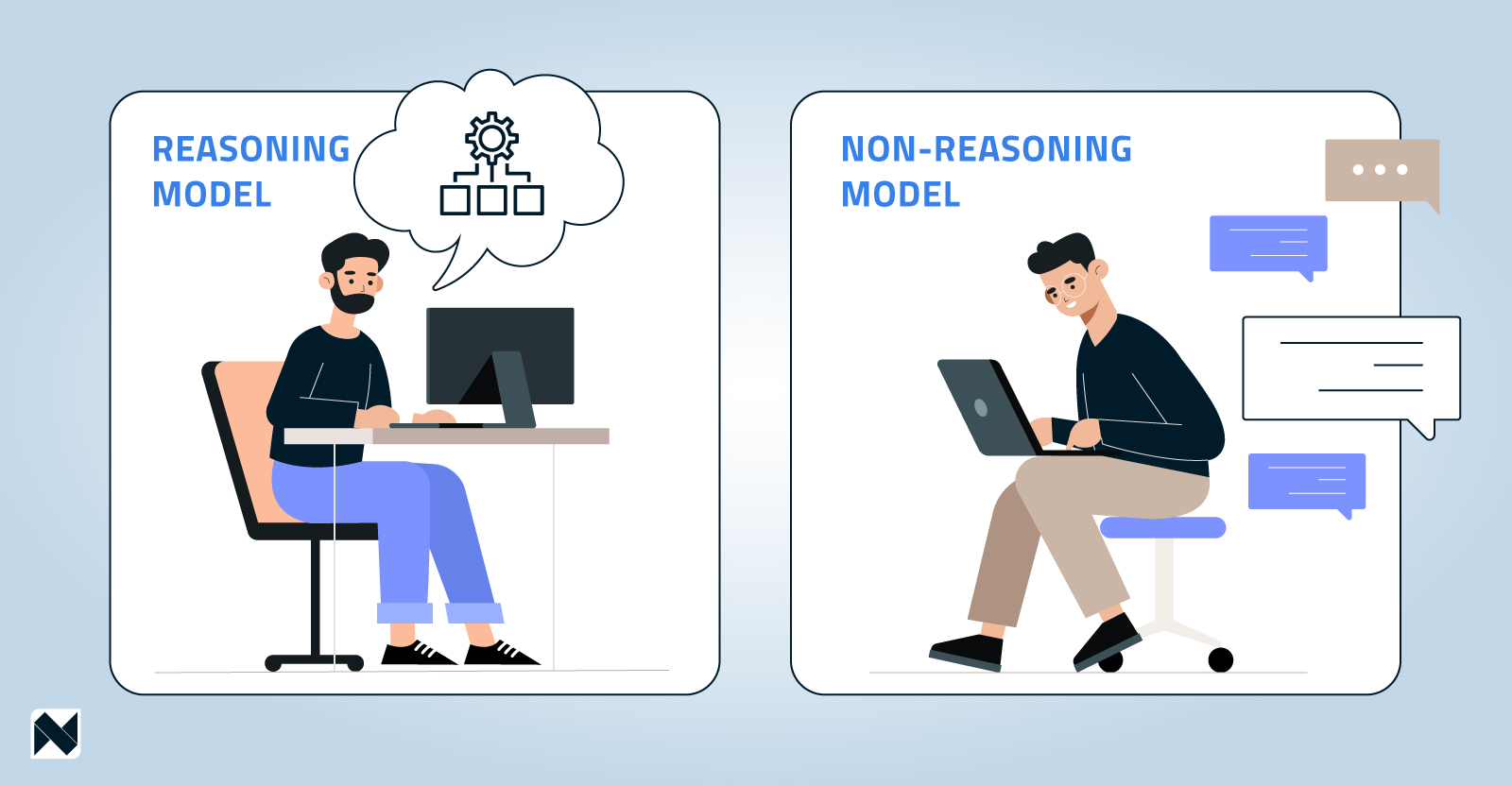
Non-reasoning models have been trained on a kind of “book” full of examples, and they stick to that book. Reasoning models are told what’s right or wrong, but not how to get there.
Does your AI think or just repeat? A real-world example
Let’s make it clear with an example. You probably use some form of AI in your daily life—whether it’s ChatGPT, DeepSeek, Claude… any of them. And not just for work, but also for everyday things or even to test and challenge the models. Here’s where the difference shows:
Imagine you type this into your AI:
oyfjdnisdr rtqwainr acxz mynzbhhx
- A non-reasoning model sees a strange string of characters and tries to match it with something it’s seen before. It might respond with random text, an error, or a guess—but it won’t get far. It doesn’t seem to understand.
- A reasoning model, on the other hand, stops and thinks:
“This looks like a cipher… maybe a code.”
It analyzes the structure, compares patterns, and decodes the hidden message:
“Think step by step.”
Same input.
Two very different approaches.
One reacts.
The other reasons.
So, which model is better?
Does all this mean reasoning models are better? Not necessarily. It depends on the kind of content you want to create. For marketing or e-commerce content—like quick replies, short answers, basic text summarization, direct translations, or mass content generation—non-reasoning models are your best bet. Why? They’re faster and don’t need to weigh different solutions.
But for fields like pharma, healthcare, law, or software, reasoning models are the way to go.
Pharma and reasoning models: a life-saving match
Reasoning models improve the accuracy of outputs—something essential in a sector like pharmaceuticals. The time it takes to generate a response isn’t what matters most—what matters is how precise that response is.
As mentioned earlier, non-reasoning models are useful for specific tasks, but pulling data from a table and drafting a safety report from it? That’s not what they’re best at.
At Narrativa, we use both types of models equally—always depending on our users’ needs and preferences.
The future lies in reasoning
It’s impossible to predict what the future will look like—especially with how fast AI is moving. But one thing is clear: the future of AI models will involve reasoning. In recent benchmarks using complex, verifiable tasks (a situation where nearly all models struggle), reasoning models are beginning to show a slight edge—as expected. In fact, most of the new models we’ve seen in the past few months are being trained with verifiable tasks to ensure reliability.
And in the future, models will be hybrid. They’ll work more like aggregators (like Perplexity), or internally using a Mixture of Experts architecture, where depending on the task, they’ll tell you which kind of model generated the response. The key will be having a choice—you’ll be able to ask the model to generate an answer using one approach or the other.
What model do we use at Narrativa?
At Narrativa, we use both types of models equally—always depending on our users’ needs and preferences.
About us
Narrativa® is an internationally recognized generative AI content automation company that believes people and artificial intelligence are better together. Its user-friendly content automation platform, equipped with built-in AI agents, empowers teams of all types and sizes to create and deploy smart composition, smart business intelligence reporting, and smart process optimization content solutions for internal and external audiences alike. Narrativa® helps teams produce content quickly and at scale, all while supporting growth across a variety of industries by saving businesses time and money. Accelerate the potential with Narrativa®.
For additional information, visit www.narrativa.com and follow on LinkedIn, Facebook, Instagram, and X.
Share